Squid Proxy is a widely-used open-source caching proxy server for the web. It is designed to improve web performance and speed up the delivery of content to clients by caching frequently-requested web pages and other Internet content, such as images and videos.
Squid Proxy works by intercepting client requests for content and then either serving the content from its cache or forwarding the request to the origin server. This helps to reduce the amount of bandwidth used by clients and improve the overall speed of the web browsing experience.
Squid Proxy is highly configurable and supports a wide range of authentication and access control methods, making it suitable for use in a variety of environments, including enterprise networks, educational institutions, and public internet access points. It also includes a number of advanced features, such as content filtering, load balancing, and SSL decryption, which make it a versatile and powerful tool for managing web traffic.
In this guide, we will learn How to Install and Configure Squid Proxy Server on CentOS | CentOS Stream | RHEL | RockyLinux | AlmaLinux 9/8
Prerequisites
- OS applies to
- CentOS 8
- CentOS Stream 8 | 9
- Rocky Linux 8 | 9
- Alma Linux 8 | 9
- User privileges: root or non-root user with root privileges.
- In this guide:
- My Network: 192.168.1.0/24
- IP Server: 192.168.1.7/24
- Hostname: linux-1
Read more
- How to Setup Static IP Address on Ubuntu Server
- How to Setup Hostname/FQDN on Linux
- How to Install and Configure LAMP stack on Ubuntu
Step 1 – Update system
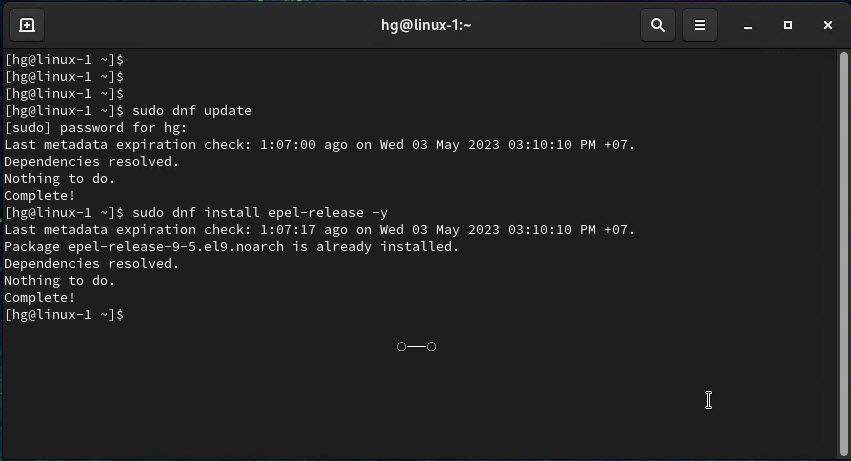
Before we start to install the OCS Inventory server on your system, we need to update the system packages to the latest versions available:
sudo dnf update
Next, install the EPEL repository with the following command:
sudo dnf install epel-release -y
Step 2 – Install Squid Proxy Server on your system
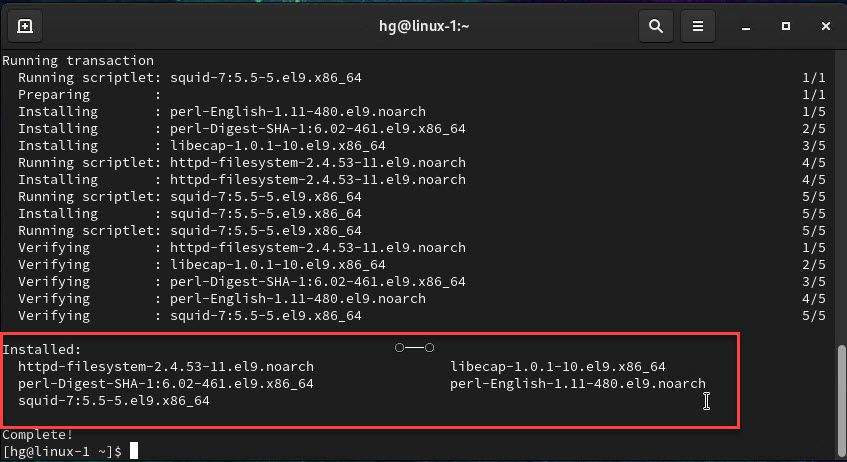
Run the following command to install Squid Proxy Server on your system:
sudo dnf install squid -y
Ensure that the Squid and its dependencies are installed on your system
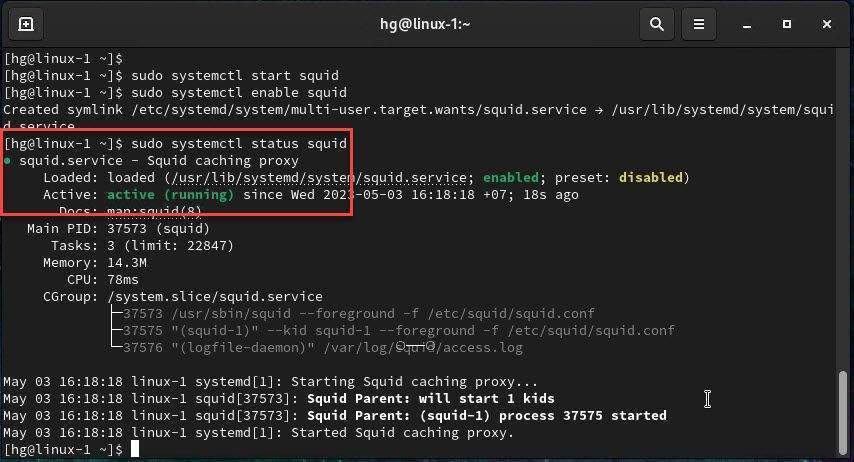
After Squid has been installed, we need to start and enable Squid service to automatically start on system startup or reboot:
sudo systemctl start squid
sudo systemctl enable squid
Check the status of the Squid service to ensure it is running by using the following command:
sudo systemctl status squid
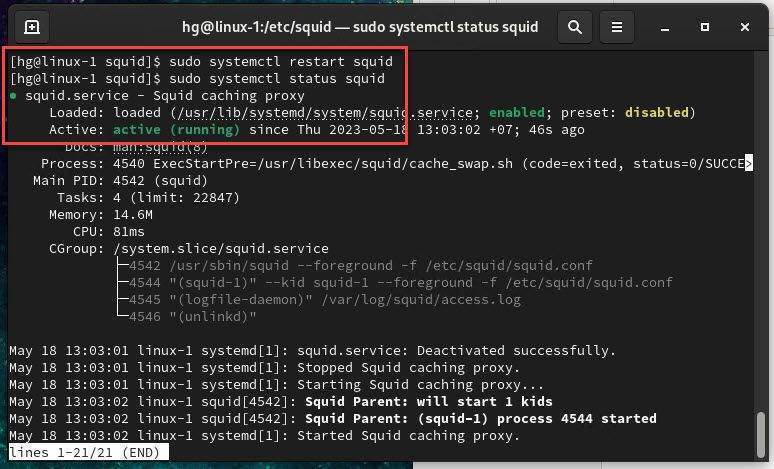
If Squid Proxy is running, you will see its status as Active as shown below:
Step 3 – Configure Squid Proxy Server
First, go to the /etc/squid directory
cd /etc/squid
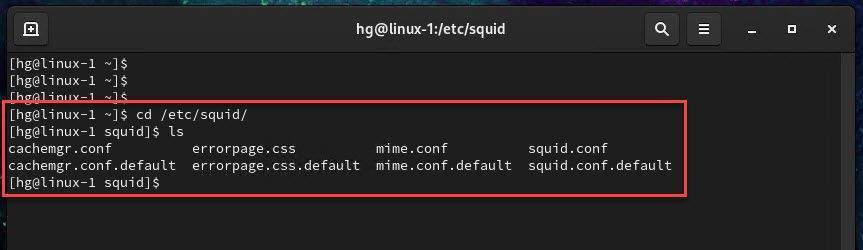
List the default installed files by using the following command:
ls
You will find the default configuration files as shown below
Next, use your favorite text editor to open the squid.conf file, in this guide, I’m using VIM editor
sudo vim squid.conf
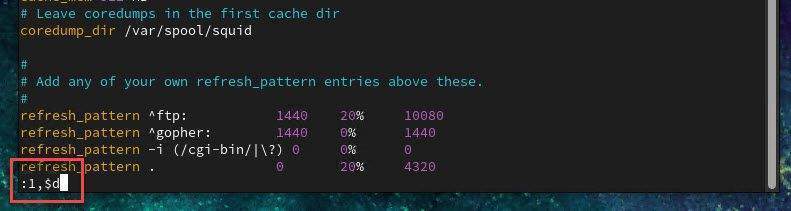
Delete all the lines in the file by pressing Esc and entering the command :1,$d then press Enter.
After that, press the i key to switch insert mode and paste the content below into the file
# # Recommended minimum configuration: # ##### Replace linux-1 = Your-hostname visible_hostname linux-1 # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt to list your (internal) IP networks from where browsing # should be allowed #acl localnet src 0.0.0.1-0.255.255.255 # RFC 1122 "this" network (LAN) #acl localnet src 10.0.0.0/8 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) #acl localnet src 100.64.0.0/10 # RFC 6598 shared address space (CGN) #acl localnet src 169.254.0.0/16 # RFC 3927 link-local (directly plugged) machines #acl localnet src 172.16.0.0/12 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) #acl localnet src 192.168.0.0/16 # RFC 1918 local private network (LAN) #acl localnet src fc00::/7 # RFC 4193 local private network range #acl localnet src fe80::/10 # RFC 4291 link-local (directly plugged) machines ##### The ACL for your network is named mylan ##### Replace 192.168.1.0 = Your-Network acl mylan src 192.168.1.0/24 acl SSL_ports port 443 acl Safe_ports port 80 # http acl Safe_ports port 21 # ftp acl Safe_ports port 443 # https acl Safe_ports port 70 # gopher acl Safe_ports port 210 # wais acl Safe_ports port 1025-65535 # unregistered ports acl Safe_ports port 280 # http-mgmt acl Safe_ports port 488 # gss-http acl Safe_ports port 591 # filemaker acl Safe_ports port 777 # multiling http # # Recommended minimum Access Permission configuration: # # Deny requests to certain unsafe ports http_access deny !Safe_ports # Deny CONNECT to other than secure SSL ports http_access deny CONNECT !SSL_ports # Only allow cachemgr access from localhost http_access allow localhost manager http_access deny manager # We strongly recommend the following be uncommented to protect innocent # web applications running on the proxy server who think the only # one who can access services on "localhost" is a local user #http_access deny to_localhost # # INSERT YOUR OWN RULE(S) HERE TO ALLOW ACCESS FROM YOUR CLIENTS # # Example rule allowing access from your local networks. # Adapt localnet in the ACL section to list your (internal) IP networks # from where browsing should be allowed #http_access allow localnet ### Allow mylan access Internet http_access allow mylan http_access allow localhost # And finally deny all other access to this proxy http_access deny all # Squid normally listens to port 3128 http_port 3128 # Uncomment and adjust the following to add a disk cache directory. cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 # Cache Men #### cache_mem = 1/3 phisycal RAM cache_mem 512 MB # Leave coredumps in the first cache dir coredump_dir /var/spool/squid # # Add any of your own refresh_pattern entries above these. # refresh_pattern ^ftp: 1440 20% 10080 refresh_pattern ^gopher: 1440 0% 1440 refresh_pattern -i (/cgi-bin/|\?) 0 0% 0 refresh_pattern . 0 20% 4320
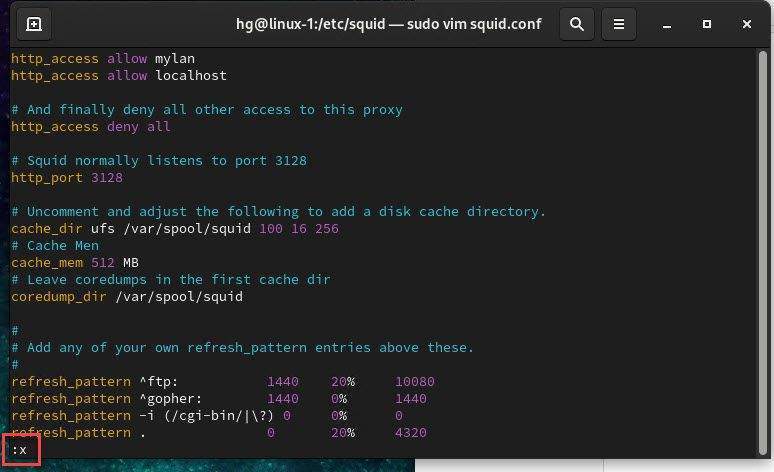
Once done, to save and exit the file, press Esc then type the command :x and press Enter
To restart the Squid Proxy service and apply the changes, use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart squid
And to ensure that the Squid service is running on your system, you can use the following command to check its status:
sudo systemctl status squid
Step 4 – Adjust Firewall
Skip this step if you do not want the firewall running on your system.
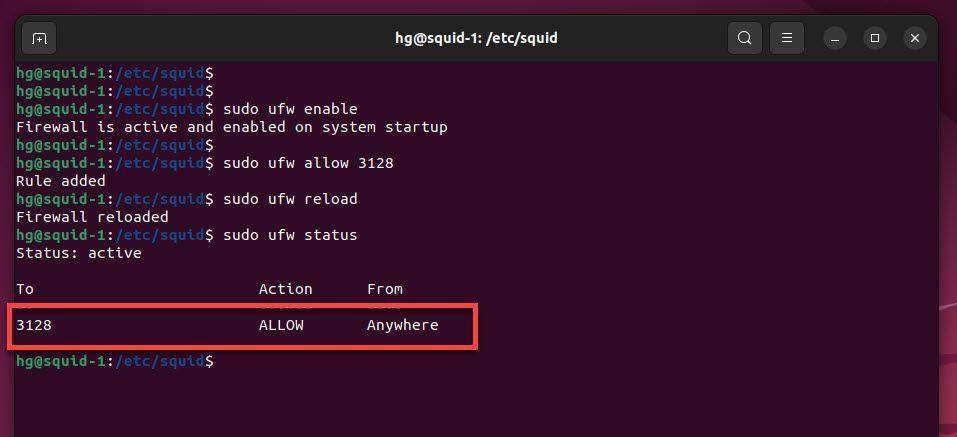
By default, Squid Proxy listens on port 3128, we need to configure to allow Squid service through the firewall using the following command:
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=squid
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
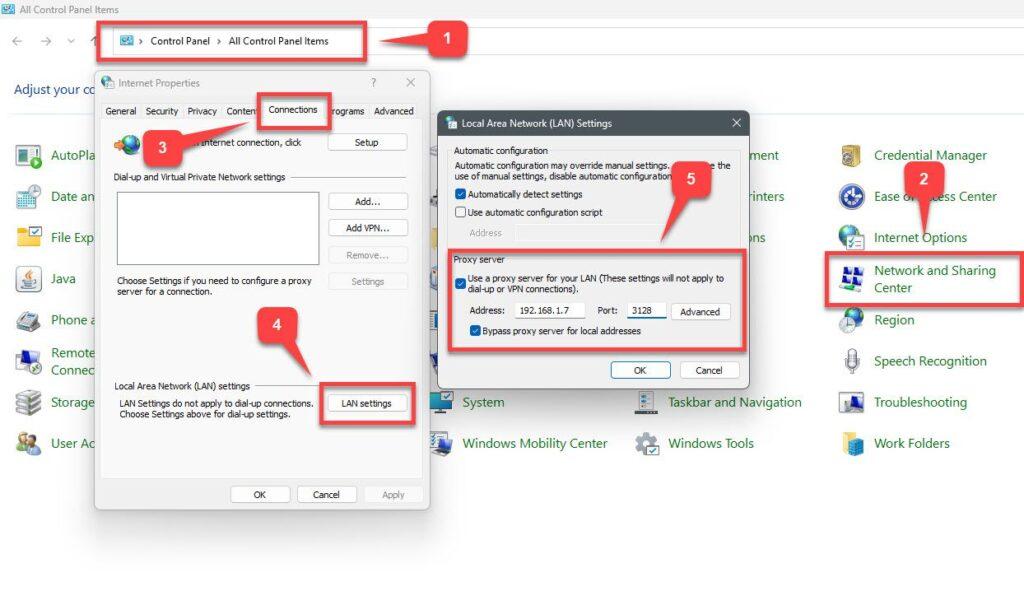
Step 5 – Configure Proxy on Windows Client
To configure a Windows client to use the proxy, access the Control Panel – Internet Options – tab Connections – button LAN Settings :
- Check to User a proxy server for your LAN ( These settings will not apply to dial-up or VPN connections)
- Address: IP-of-the-Squid-Proxy-Server
- Port: 3128
That’s it! With this article, you now have the knowledge to set up a Squid Proxy on CentOS | CentOS Stream | RockyLinux | AlmaLinux by yourself.
Thank you for reading !!!