LEMP is an open-source web application stack used to develop web applications. The term LEMP is an acronym that represents L for the Linux Operating system, Nginx (pronounced as engine-x, hence the E in the acronym) web server, M for MySQL/MariaDB database, and P for PHP scripting language.
LEMP stands for:
- L – Linux Operating System
- E – Nginx Server
- M – MySQL/MariaDB database or MariaDB database
- P – PHP programming language
In thi article, We will learn How to Install LEMP stack on Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04 | 18.04 LTS
Prerequisites
- Operating system: A Ubuntu Desktop or Ubuntu Server installed
- User privileges: root or non-root user with sudo privileges
Step 1 – Update system
First of all, ensure everything is up to date on your server
sudo apt update
Step 2 – Install Nginx Web server
To install the Nginx Web server on your server execute the following command:
sudo apt install nginx -y
Once the package installer has finished, We need start and enable Apache service to auto-start on system restart or boot:
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginx
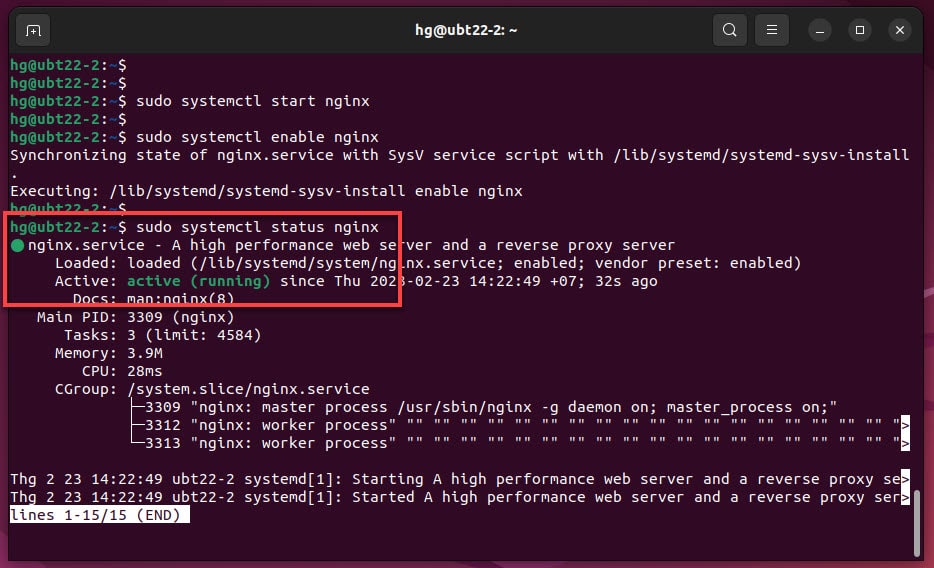
Check status of Nginx service, make sure it’s running:
sudo systemctl status nginx
If running, result as like below:
By default, Nginx listens to incoming HTTP connections on port 80 and port 443 for secure connections. We need to allow HTTP port 80 and HTTPS port 443 through the UFW firewall.
Skip this step, If you don't want to the UFW firewall running on the system.
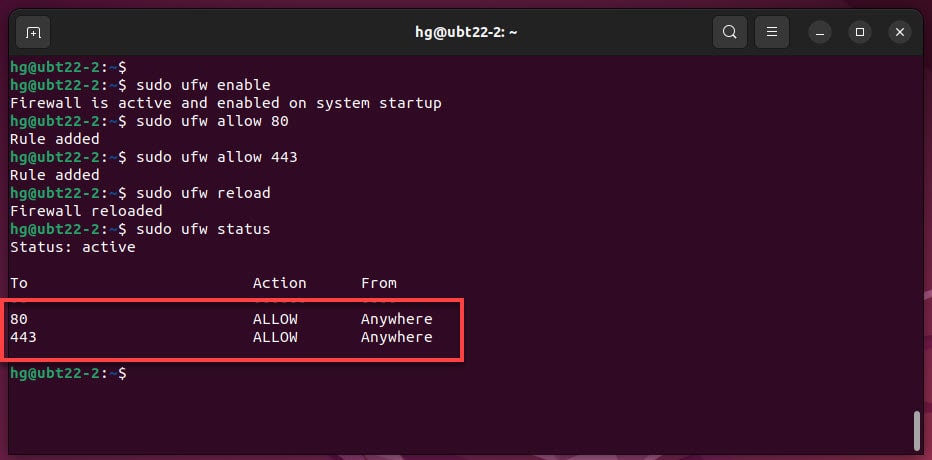
sudo ufw enable ### Enable the Firewall if it not yet running
sudo ufw allow 80 ### Allow port 80
sudo ufw allow 443 ### Allow port 443
sudo ufw reload ### Reload firewall
sudo ufw status ### Check status of Firewall
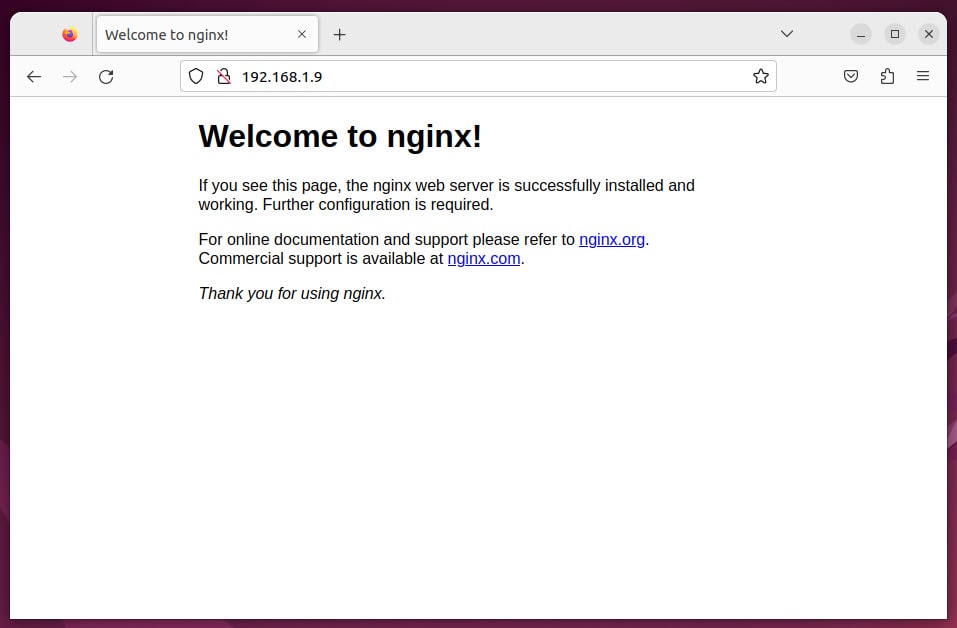
Now, open your browse and access address http://IP-Server to test Nginx web server
http://IP-Server
If you receive the page below, it means you have successfully installed the Nginx server.
Step 2 – Install MySQL/MariaDB database server
In this tutorial, We will install MariaDB server, to install execute the following command:
sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-client -y
MySQL/MariaDB database server installed, we need to start and enable it to auto-start on system restart or boot:
sudo systemctl start mariadb
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
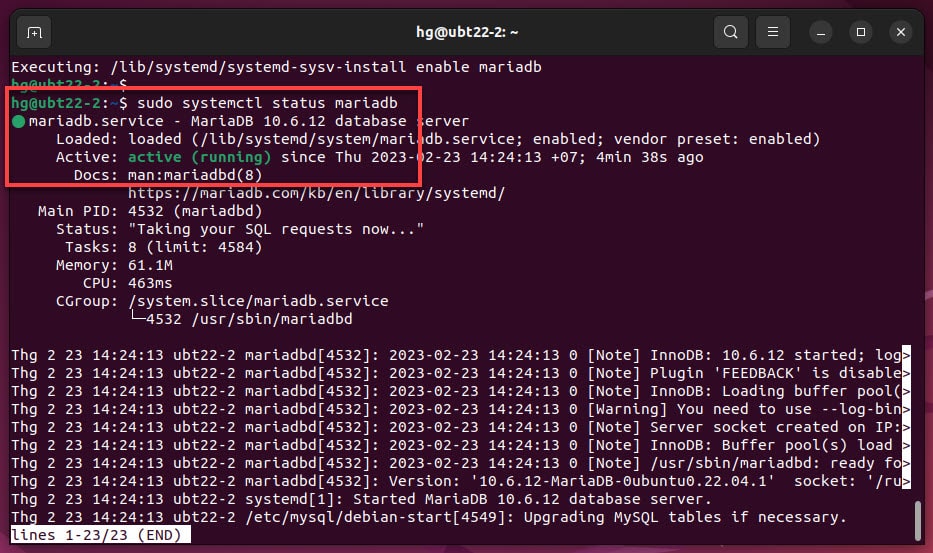
Check status of MySQL/MariaDB server, make sure it’s running:
sudo systemctl status mariadb
If running, you will see a green Active status like below.
Next, you need to configure security for MySQL/MariaDB server by following command below:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
And confirm the questions below:
hg@ubt22-1:~$ sudo mysql_secure_installation NOTE: RUNNING ALL PARTS OF THIS SCRIPT IS RECOMMENDED FOR ALL MariaDB SERVERS IN PRODUCTION USE! PLEASE READ EACH STEP CAREFULLY! In order to log into MariaDB to secure it, we'll need the current password for the root user. If you've just installed MariaDB, and haven't set the root password yet, you should just press enter here. Enter current password for root (enter for none): ### Enter OK, successfully used password, moving on... Setting the root password or using the unix_socket ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB root user without the proper authorisation. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n] n ### Type n and press Enter ... skipping. You already have your root account protected, so you can safely answer 'n'. Change the root password? [Y/n] y ### Type y and press Enter New password: ### Enter Password for root Re-enter new password: ### Re-nter Password for root Password updated successfully! Reloading privilege tables.. ... Success! By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a production environment. Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] ### Press Enter ... Success! Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from 'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network. Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] ### Press Enter ... Success! By default, MariaDB comes with a database named 'test' that anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed before moving into a production environment. Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] ### Press Enter - Dropping test database... ... Success! - Removing privileges on test database... ... Success! Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far will take effect immediately. Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] ### Press Enter ... Success! Cleaning up... All done! If you've completed all of the above steps, your MariaDB installation should now be secure. Thanks for using MariaDB! hg@ubt22-1:~$
Step 4 – Install PHP
You have Nginx installed to serve your content and MariaDB installed to store and manage your data. Now you can install PHP to process code and generate dynamic content for the web server.
To install the PHP along with extensions execute the following command:
sudo apt install php php-fpm libapache2-mod-php php-mysql php-mbstring -y
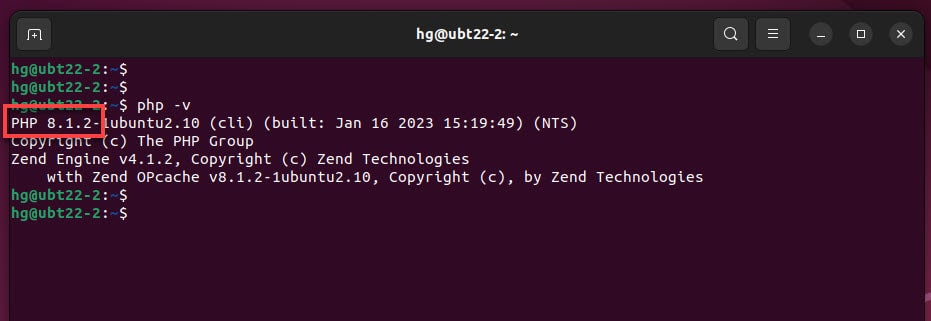
Check the PHP version, by default PHP 8.1 installed on Ubuntu 22
php -v
Next, start PHP-FPM and enable it to start automatically at boot time:
sudo systemctl start php8.1-fpm
sudo systemctl enable php8.1-fpm
Check status of PHP-FPM service, make sure it’s running:
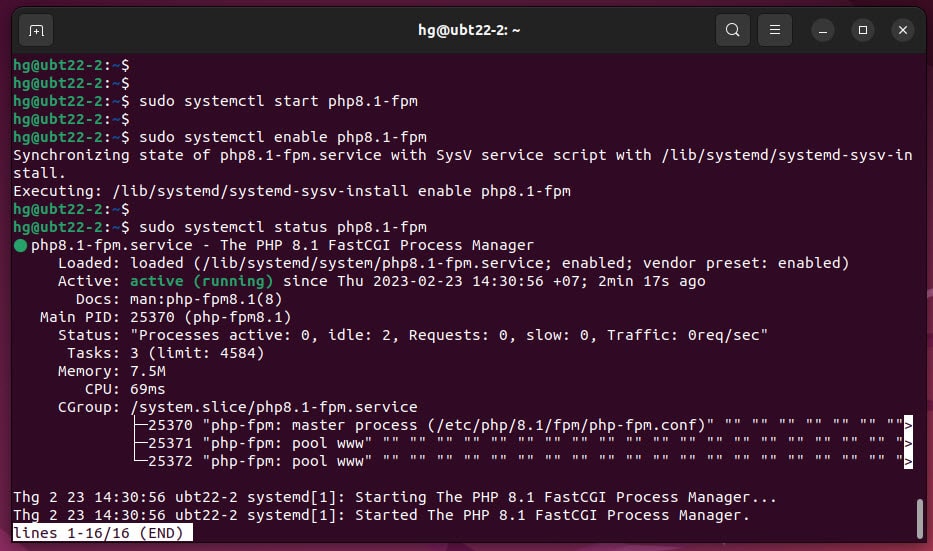
sudo systemctl status php8.1-fpm
If running, result as like below:
That’s it. you are install successfully LEMP stack on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS | 20.04 LTS | 18.04 LTS
Read more:
- Install Docker and Portainer on Raspberry Pi
- How to Install LEMP Stack on Ubuntu/Debian
- Understanding TrueNAS RAID Levels: Stripe, Mirror, RAIDZ, and dRAID Explained
- Samba – Part 3 – Set Up Samba with Separate Read/Write Access for Each User
- Samba – Part 2 – Share a Folder with Read and Write Access in LAN
Thank you for reading !!!